The restoration of decorative plasters and moldings is a complex process that requires advanced knowledge and professional skills to ensure quality and long-lasting results. One of the essential methods used in this process is reinforcement by anchors and nets. This article will detail the main tasks of a conservator at this crucial stage.
Preparation of the material required for surface reinforcement
Preparing the materials for consolidation is the first important step in ensuring the success of the intervention. The restorer must select the appropriate materials that comply with the technical specifications and requirements of the project. These include anchors, nets, adhesives and other fastening materials, which must be of high quality to guarantee the durability of the work.
Marking of intervention/consolidation sites
The precise marking of the intervention sites is crucial for a correct execution of the reinforcement works. The restorer uses the technological map to identify and mark the areas that require intervention. This stage involves detailed planning and in-depth knowledge of the structure and condition of decorative plaster and moldings. Correct marking ensures that all affected areas are treated properly and that interventions are carried out exactly where they are needed.
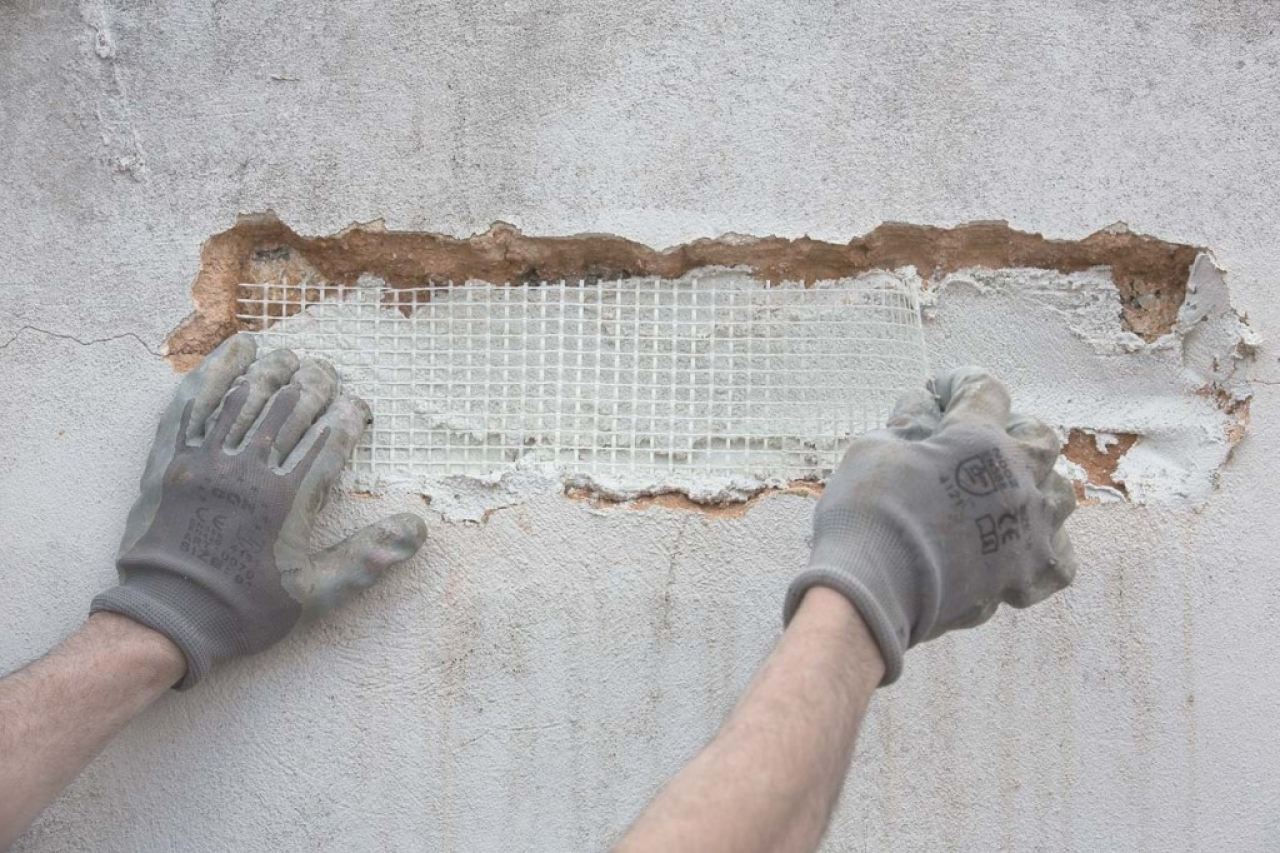
Carrying out consolidation works with the use of anchors/nets
Carrying out reinforcement work involves the use of anchors and nets to stabilize and strengthen the structure of the decorative plaster. This method involves fixing the mesh to the surface of the plaster and using anchors to ensure strong adhesion between the reinforcing mesh and the wall substrate. The restorer must be very precise and careful at this stage to avoid further damage and ensure optimal fixation.
Quality assurance of consolidation works
The quality of the consolidation work is essential for the long-term success of the restoration. The restorer must constantly monitor the quality of the work to ensure that all interventions are carried out to the highest standards. This includes checking the adhesion of anchors and nets, assessing the uniformity and durability of reinforcement, as well as detailed documentation of each step of the process.
Conclusion
The professional competence of a decorative plaster and molding restorer is essential for the success of the restoration process. By preparing materials, marking the places of intervention, carrying out consolidation works with the use of anchors and nets and ensuring the quality of the works, the restorer contributes significantly to the preservation and revitalization of the cultural heritage. Following these rigorous procedures and attention to detail are fundamental to achieving long-lasting, high-quality results.