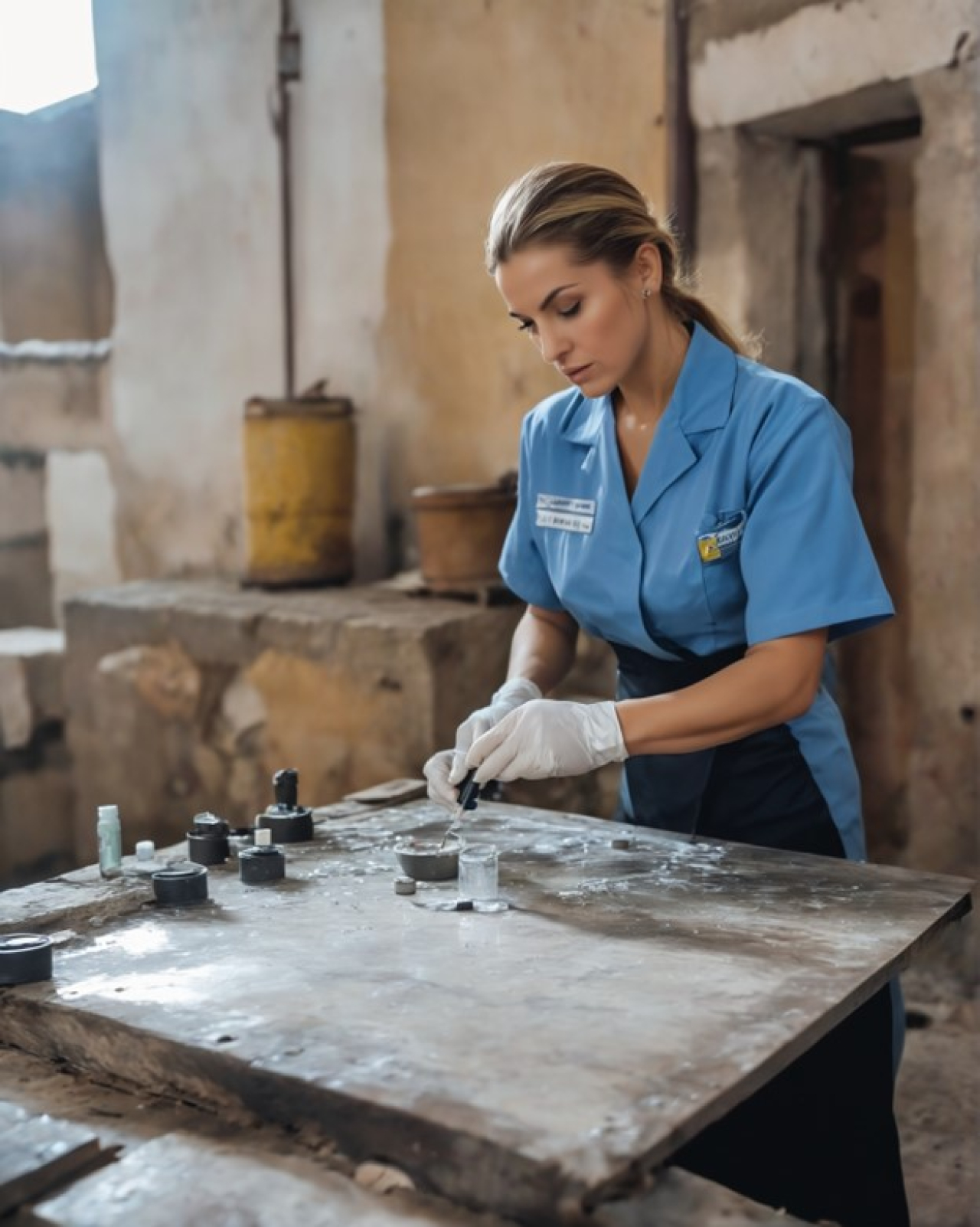
The restoration of decorative plasters and moldings is a particularly specialized field in which professional competence and attention to detail are essential. The injection of reinforcing materials is a critical step in the restoration process that requires rigorous preparation and precise execution. Next, we will detail the main tasks of a restorer at this stage.
Removing potential risks
A competent conservator always starts by identifying and removing potential risks from the work area. This step is vital to ensure a safe working environment, protecting both the integrity of the work and the safety of the team. As part of this task, the restorer carefully inspects the intervention area to identify and eliminate any possible hazards that could compromise the restoration process or cause accidents.
Preparation of the material required for surface reinforcement
The preparation of reinforcement materials is an essential step that ensures the success of the intervention. The restorer carefully selects the right materials, according to the technical specifications and requirements of the project. These materials must be of high quality and correspond to the original characteristics of decorative plaster and moldings. The restorer also ensures that the materials are prepared correctly, complying with all safety rules and procedures.
Marking of intervention/consolidation sites
The precise marking of the intervention sites is crucial for a correct execution of the reinforcement works. The restorer uses the technological map to identify and mark the areas that require intervention. This stage involves detailed planning and an in-depth knowledge of the structure and condition of the decorative plaster and moldings, thus ensuring that all affected areas are treated properly.
Injection of the material at the location indicated in the technology map
Injecting reinforcing materials into marked places is a delicate operation that requires precision and skill. The restorer follows the technology map and uses specialized equipment to inject the reinforcing material into the affected areas. This process must be carried out carefully to ensure an even distribution of the material and to avoid further damage to the plaster.
Quality assurance of consolidation works
The quality of the consolidation works is constantly monitored by the restorer to guarantee that all interventions are carried out to the highest standards. This includes checking the adhesion of the materials, assessing the uniformity of the injection and ensuring that all technical specifications are followed. The conservator documents every step of the process, thus providing a solid basis for the final evaluation of the work.
Conclusion
The professional competence of a decorative plaster and molding restorer is essential for the success of the restoration process. By removing risks, preparing materials, marking intervention sites, precisely injecting reinforcing materials and ensuring the quality of the works, the restorer contributes to the preservation and revitalization of cultural heritage. Following these rigorous procedures and attention to detail are fundamental to achieving long-lasting, high-quality results.