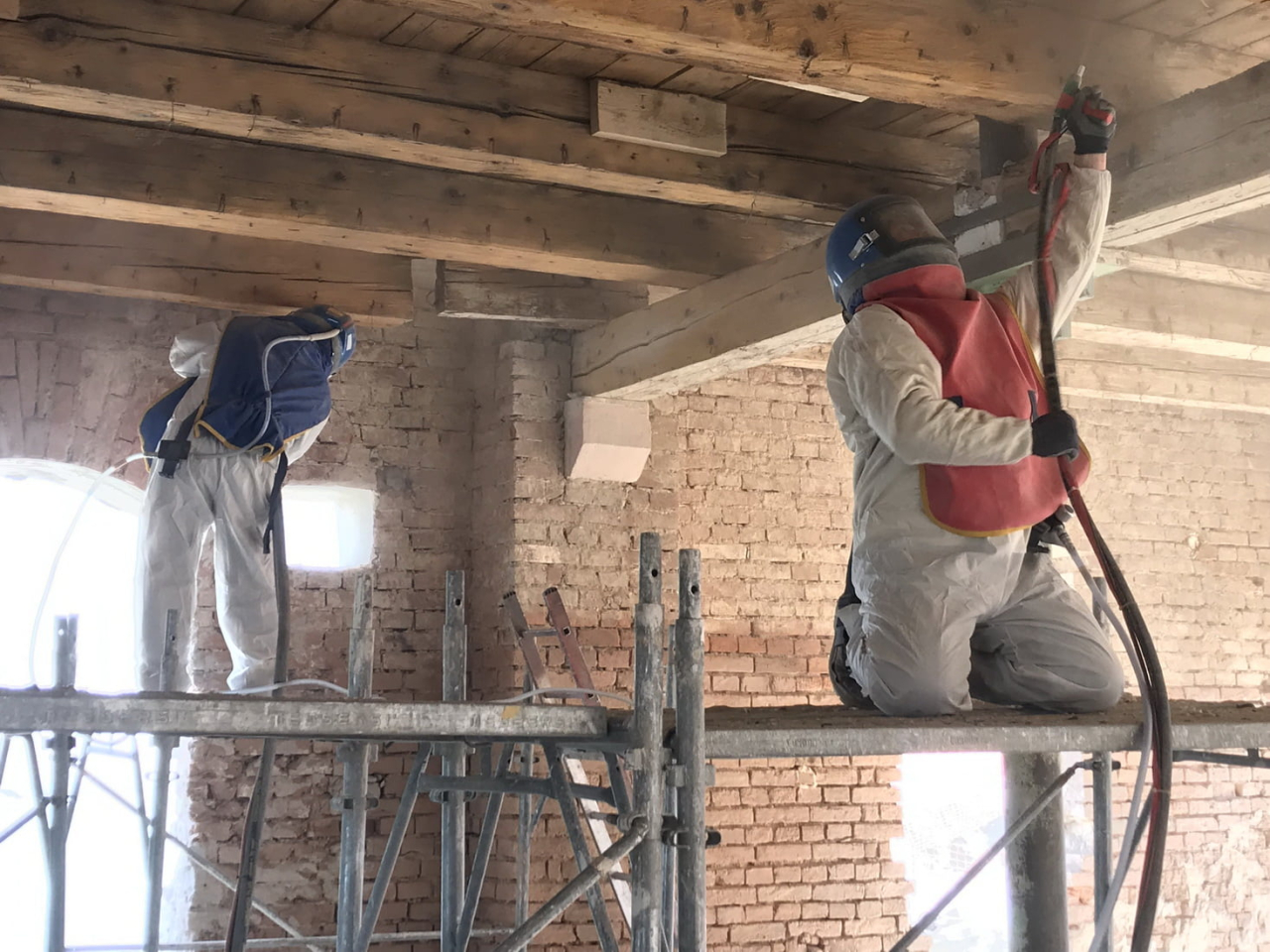
Professional competence of a Restorer of decorative plasters and modernature: Applying the rules of protection of monuments and environmental protection
The restoration of cultural heritage involves not only technical and artistic skills, but also a strong commitment to the protection of monuments and the environment. Restorers of decorative plasters and modernity must comply with strict rules to ensure the sustainable preservation of historic buildings and minimise their impact on the environment. Here are some of the essential professional skills in this area:
Rational use of natural and energy resources
One of the fundamental aspects of environmental protection is the efficient and rational use of natural and energy resources. Restaurateurs must be aware of the consumption of water, energy and materials and adopt sustainable practices in their work. This can include using eco-friendly materials, optimizing work processes to reduce energy consumption, and implementing modern technologies that minimize environmental impact.
Usage of reusable material on recovery procedures
In the restoration process, many materials can be recovered and reused, thus helping to reduce waste and protect natural resources. Restorers must be familiar with recovery techniques and implement appropriate procedures to maximize the reuse of materials. Not only is this beneficial for the environment, but it can also reduce the costs associated with purchasing new materials.
Storage of production waste in specially arranged places
Proper management of waste generated during restoration is essential for environmental protection. All waste must be collected and stored in specially arranged places, according to the regulations in force. Restorers must ensure that these practices are strictly adhered to to prevent soil and water contamination and to protect public health.
Intervention in work or environmental accident/incident
In the event of a work or environmental accident or incident, restorers must be prepared to intervene promptly and efficiently. This includes knowledge of emergency procedures, the use of appropriate equipment and coordination with the relevant authorities. Rapid and effective interventions can minimise negative environmental impacts and protect the safety of staff and the public.
Conclusion
The professional skills of a restorer of decorative plasters and molding are multiple and complex, including the application of monument protection and environmental protection rules. Through the rational use of natural and energy resources, the application of procedures for the recovery of reusable materials, the correct management of waste and prompt intervention in case of accidents, restorers contribute to the sustainable preservation of cultural heritage and to the protection of the environment. These competencies not only ensure the integrity and longevity of historic buildings, but also demonstrate a deep commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility.